
Fluid-structure interactions are numerous in the cerebrospinal system and difficult to understand in the rigid skull. Simulation results show a significant variability of aqueduct stroke volume and intracranial subarachnoid space stroke volume in the physiological range of cardiac frequencies. CSF velocity and pressure and brain displacements are obtained as simulation results, and CSF flow and stroke volume are calculated from these results. The model geometry, simplified in a first approach, is designed in accordance with realistic volume ratios of the different compartments: a thin tube is used to mimic the high flow resistance of the aqueduct. A numerical fluid-structure interaction model is implemented using a finite-element method library to model the cerebrospinal system and its interaction with the brain based on fluid mechanics equations and linear elasticity equations coupled in a monolithic formulation. To study this CSF distribution, we have developed a numerical model of the cerebrospinal system taking into account cerebral ventricles, intracranial subarachnoid spaces, spinal canal and brain tissue in fluid-structure interactions. The amplitude of the CSF oscillations through the different compartments of the cerebrospinal system is a function of the geometry and the compliances of each compartment, but we suspect that it could also be impacted be the cardiac cycle frequency. In a healthy population, aqueduct stroke volume represents around 10% of the spinal stroke volume while intracranial subarachnoid space stroke volume represents 90%. Garnotel, Simon Salmon, Stéphanie Balédent, OlivierĬerebrospinal fluid (CSF) stroke volume in the aqueduct is widely used to evaluate CSF dynamics disorders.
Numerical Cerebrospinal System Modeling in Fluid-Structure Interaction. Therefore, research is increasingly aided. The investigation via experiments is costly, difficult or in some cases, even impossible.
The fluid-structure interaction (FSI) of this kind is frequently encountered in injection molding, food processing, pharmaceutical engineering and biomedicine. The investigated complex fluids are non-Newtonian viscoelastic fluids. In the present work the interaction between rheologically complex fluids and elastic solids is studied by means of numerical modeling.
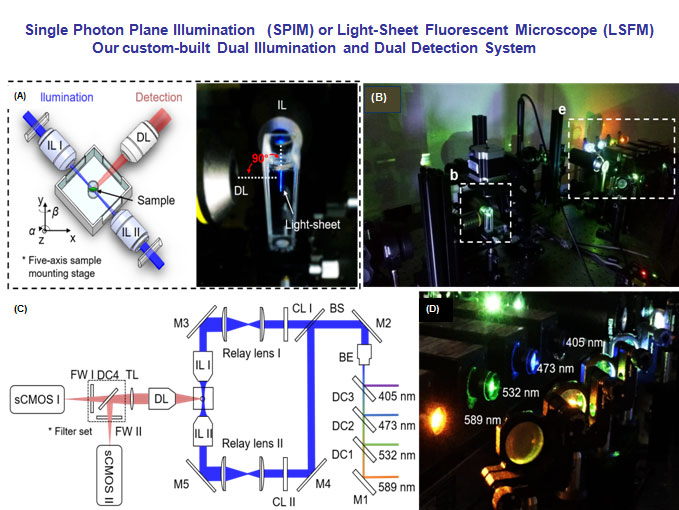
Numerical Modeling of Fluid-Structure Interaction with Rheologically Complex Fluids


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
